Estimation Activities for Special Education
Teaching Estimation to Children with Special Needs
Children with special needs encompass a diverse spectrum of abilities and challenges, including but not limited to autism spectrum disorders, ADHD, dyslexia, and intellectual disabilities. Traditional teaching methods may not always cater to their unique learning styles and requirements. When it comes to estimation, which involves approximating quantities or values, these children may face hurdles due to difficulties in processing information, spatial reasoning, or attention deficits. It can be a confusing concept to simply give a guess (well, an educated guess) rather than actually counting the objects, which is what they’ve been practicing since they learned to count!
Effective teaching of estimation for children with special needs hinges on individualized, adaptable strategies that cater to their specific needs and strengths. Here are some approaches educators can try to use in their classroom:
Visual Aids and Manipulatives: Utilizing visual aids such as pictures, diagrams, or physical objects can enhance understanding and engagement. For instance, using colorful blocks or counting beads to represent quantities makes estimation tangible and interactive.
Structured Activities: Breaking down estimation tasks into manageable steps with clear instructions helps in maintaining focus and reducing anxiety. Providing structured activities with visual cues can guide children through the estimation process systematically.
Multi-Sensory Learning: Incorporating multi-sensory experiences, including touch, sight, and sound, can facilitate better comprehension and retention. For instance, involving music or rhythm in estimation games adds an enjoyable dimension to learning.
Real-World Applications: Relating estimation to real-life scenarios that children encounter daily fosters practical understanding and relevance. Whether it's estimating the number of cookies in a jar or the distance to a familiar landmark, connecting concepts to their lived experiences enhances comprehension.
Positive Reinforcement and Patience: Celebrating small victories and providing positive reinforcement play crucial roles in building confidence and motivation. Patience is key, as children may require more time to grasp concepts or may benefit from repeated practice sessions.
Estimation Activities for Special Education
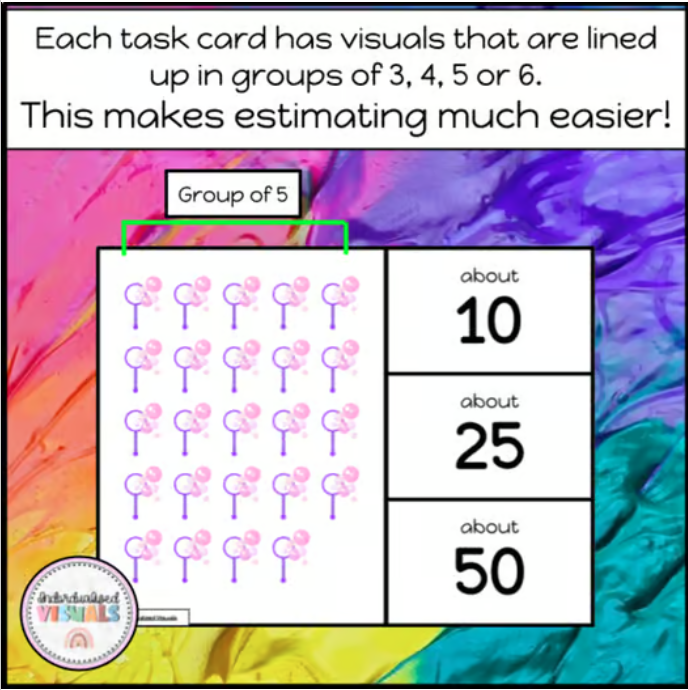
Estimation Task Cards
These 20 estimation task cards include visuals in groups of 3-6, which make estimating much easier for our students! Each task card also includes 3 options (ex. about 10, about 20 or about 35) that the student can choose from by putting a clothes peg on their answer. These task cards are super engaging because they include visuals of common preferred items such as video game controllers, unicorns, pizza & more!
Each task card has visuals lined up in groups of 3, 4, 5 or 6, which makes estimating much easier for our students! Then they are given 3 options to choose from for their educated guess of how many of the object there are. This is a great first step in estimating!
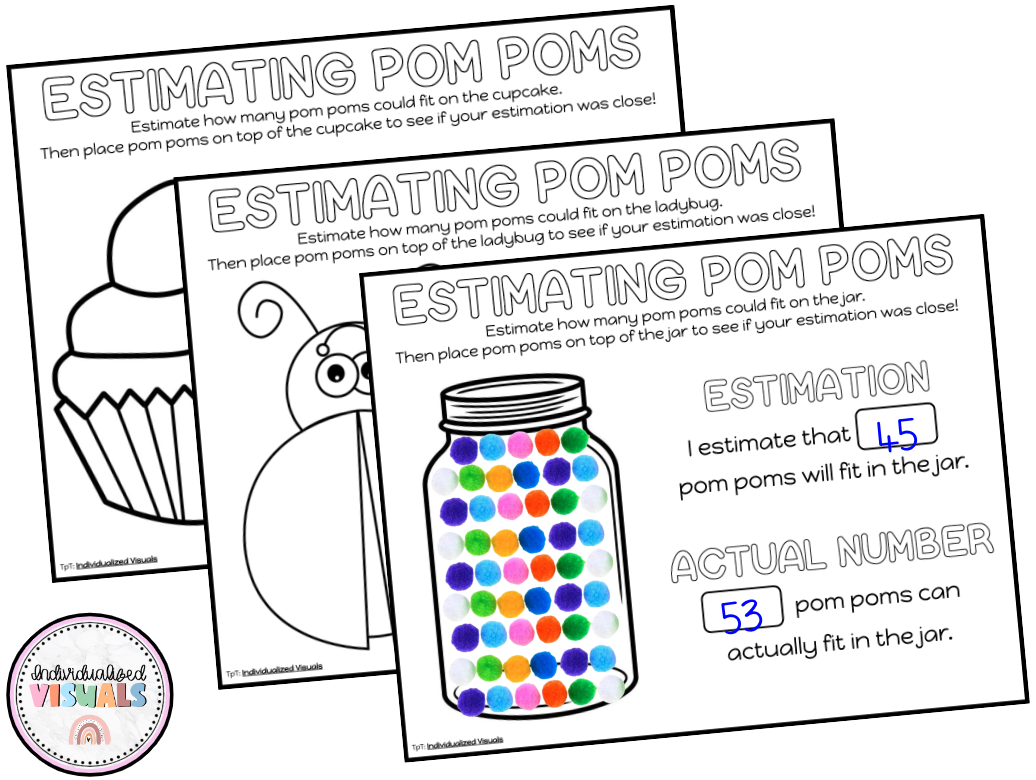
Estimation Worksheets
These 10 estimation worksheets challenge students to estimate how many pom pom balls could fit in each object on their page! Then they can place pom poms close together on the object to see how close their guess was!
Students will estimate how many pompom balls would fit on top of the image if they line them up close together. Then they will actually take pompoms and place them on the image, and count them!